The Rise of Telehealth Robotics
In 2025, telehealth robots are transforming how healthcare is delivered, enabling doctors to provide remote medical assistance with unprecedented precision and efficiency. These advanced robotic systems, equipped with high-definition cameras, microphones, and mobility features, are bridging geographical gaps and making specialized care accessible to patients in remote or underserved areas. 'Telehealth robots represent the next frontier in medical technology, allowing us to extend our expertise beyond hospital walls,' says Dr. Sarah Mitchell, a telemedicine specialist at Johns Hopkins Hospital.
How Telehealth Robots Work
Telehealth robots function as mobile telepresence units that allow healthcare professionals to conduct virtual consultations, monitor patients in real-time, and even assist in surgical procedures from remote locations. These systems typically include 360-degree cameras, high-quality audio systems, and autonomous navigation capabilities. Research from Proven Robotics shows that these robots can navigate hospital corridors independently, allowing doctors to 'virtually walk' through facilities and interact with patients and staff.
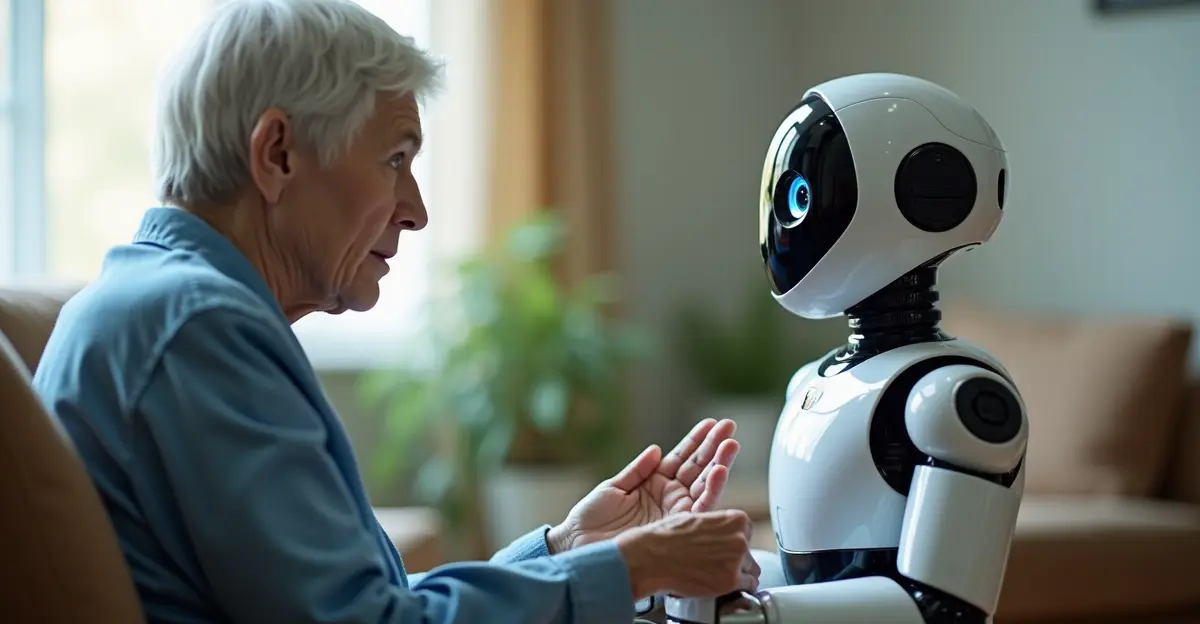
The technology integrates with existing hospital infrastructure, connecting to electronic health records and diagnostic equipment. 'What makes these systems revolutionary is their ability to provide the human touch remotely,' explains robotics engineer Michael Chen. 'Doctors can make eye contact with patients, read body language, and establish meaningful connections despite the physical distance.'
Real-World Applications and Benefits
Remote Patient Monitoring
Telehealth robots are particularly valuable for continuous patient monitoring in intensive care units and long-term care facilities. They can perform routine checks, monitor vital signs, and alert medical staff to changes in patient condition. According to Robotics Tomorrow, the medical telepresence robot market is projected to grow from $75 million in 2024 to $116.47 million by 2034, reflecting increasing adoption across healthcare settings.
Surgical Assistance and Consultations
Advanced telehealth robots are now capable of assisting in surgical procedures by providing real-time video feeds and enabling remote specialists to guide local surgeons. 'During complex procedures, having instant access to specialists from around the world can be life-saving,' notes Dr. Elena Rodriguez, a cardiac surgeon who regularly uses telehealth robots for consultations. The systems allow for precise measurements and annotations directly on the surgical field view.
Rural and Underserved Communities
For patients in rural areas or communities with limited access to specialists, telehealth robots are breaking down barriers to quality care. A National Academy of Medicine case study highlights how these technologies are particularly beneficial for patients who face transportation challenges or live in areas with healthcare provider shortages.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Technical and Infrastructure Requirements
Successful implementation of telehealth robots requires robust internet connectivity and proper hospital infrastructure. 'The biggest challenge isn't the robots themselves, but ensuring reliable 5G networks and adequate bandwidth,' says technology consultant David Park. Hospitals need to invest in network upgrades and staff training to maximize the benefits of these systems.
Regulatory and Privacy Concerns
Data privacy and cross-jurisdictional practice remain significant concerns. Industry analysis indicates that healthcare organizations must navigate complex regulatory frameworks while ensuring patient data security. 'We're working closely with regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines for telehealth robot usage,' explains healthcare attorney Maria Gonzalez.
Cost and Training Considerations
While initial investment costs can be substantial, studies show that telehealth robots can lead to significant long-term savings by reducing travel expenses and improving resource allocation. 'The return on investment becomes clear when you consider reduced patient transfer costs and improved specialist utilization,' says hospital administrator Robert Thompson.
The Future of Telehealth Robotics
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence with telehealth robots promises even greater advancements. Recent research indicates that AI-enhanced robots will be able to perform preliminary diagnostics, monitor multiple patients simultaneously, and provide personalized care recommendations. The global medical robotics market is projected to grow from $14.9 billion in 2023 to $57.0 billion by 2032, with telehealth robots representing a significant portion of this expansion.
'We're just scratching the surface of what's possible,' concludes Dr. Mitchell. 'As technology continues to evolve, telehealth robots will become increasingly sophisticated, offering new ways to deliver compassionate, effective care to patients wherever they are.'

 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português