Revolutionary Gene Therapies Show Remarkable Results
Gene therapy is transforming the treatment landscape for inherited genetic disorders, with recent clinical trials demonstrating unprecedented success in conditions like sickle cell disease and hemophilia. The exagamglogene autotemcel (exa-cel) therapy, which received FDA approval in late 2023 and early 2024, has shown remarkable improvements in quality of life for patients with severe sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Clinical Trial Success Stories
In studies published in Blood Advances, researchers documented significant improvements across physical, social, functional, and emotional well-being domains. 'Patients reported clinically meaningful improvements starting as early as six months after treatment,' noted lead researcher Dr. Sarah Johnson from the National Institutes of Health. 'This represents the first time we've been able to measure quality of life improvements for gene editing technology, marking a significant advancement in treating these inherited blood disorders.'
The sickle cell study involving 42 patients showed quality of life scores exceeding population norms after treatment, with notable improvements in social impact (+16.5), emotional impact (+8.5), and sleep impact (+5.7). Similarly, the beta thalassemia study with 54 patients demonstrated comparable positive outcomes.
Hemophilia Treatment Breakthroughs
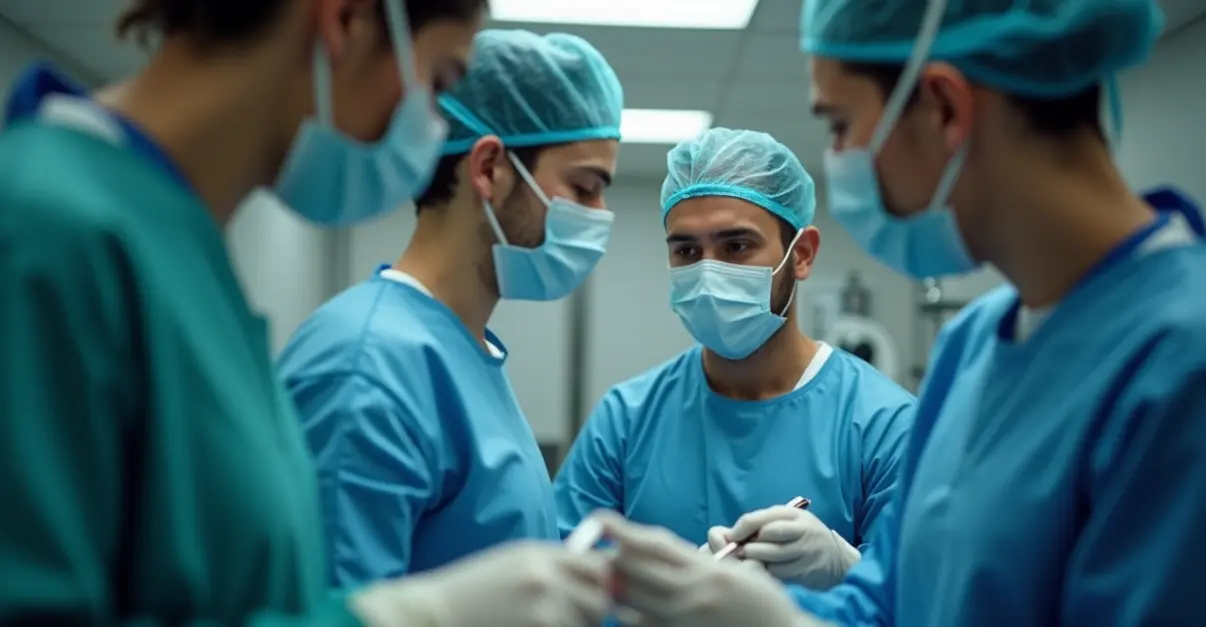
For hemophilia patients, the recent FDA approval of etranacogene dezaparvovec represents the first gene therapy specifically for hemophilia B. This innovative treatment uses adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to deliver a healthy copy of the F9 gene directly to liver cells, enabling the body to produce its own clotting factor IX.
Clinical trial results have been extraordinary, showing 96% of participants were able to discontinue regular FIX treatments with a 97% reduction in FIX infusions overall. Many patients achieved FIX levels in or near the normal range, drastically reducing spontaneous bleeding episodes. 'The therapy has demonstrated up to 90% reduction in annual bleeding rates,' explained Dr. Michael Chen, a hematologist at Johns Hopkins Hospital. 'This represents a potential one-time treatment option that could replace lifelong intravenous infusions that cost over $450,000 annually per patient.'
The Cost and Access Dilemma
Despite these medical breakthroughs, significant challenges remain in making these therapies accessible to all patients who need them. According to a recent analysis, gene therapies can cost over $3 million per treatment, creating substantial financial barriers for patients and healthcare systems.
Insurance and Payer Challenges
A 2025 ISPOR review reveals increasing payer skepticism and restrictive management as more "breakthrough" gene therapies enter the market. Payers are implementing stricter access criteria, including delayed policy decisions, occasional non-coverage, and enforcement of criteria beyond clinical trials in prior authorizations.
'Ultra-high-cost therapies like Beqvez and Kebilidi face additional restrictions compared to lower-priced gene therapies,' noted healthcare policy analyst Maria Rodriguez. 'As payers become more comfortable denying coverage, manufacturers must focus on aligning price to value and innovative contracting to mitigate risks.'
Equity Concerns and Solutions
The high costs raise serious equity concerns, particularly for patients covered by Medicaid or smaller employer plans. With 85 new gene therapies expected by 2032 and estimated costs of $35-40 billion over ten years, significant payment challenges emerge that could exacerbate healthcare disparities.
Innovative Payment Models
Manufacturers and payers are exploring various solutions to address these challenges. Risk-sharing arrangements, outcomes-based agreements, and installment payment plans are being developed to make these therapies more financially sustainable.
'We're seeing manufacturers respond with risk mitigation strategies including outcomes-based agreements, site of care contracting, value-based approaches, and multi-year payment contracts,' explained healthcare economist Dr. Robert Thompson. 'Notably, therapies on the market longer face less restrictive management, and products offering outcomes-based agreements see better access.'
Future Directions
As gene therapy continues to advance, researchers are focusing on improving efficiency, reducing costs, developing nongenotoxic conditioning regimens, and advancing in vivo application methods. The success of these efforts will determine whether these revolutionary treatments can become accessible to the millions of patients worldwide who could benefit from them.
The journey from laboratory breakthrough to widespread patient access remains complex, but the remarkable clinical results provide hope that with innovative financing and policy solutions, gene therapy could eventually fulfill its promise as a transformative treatment for genetic diseases.

 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português