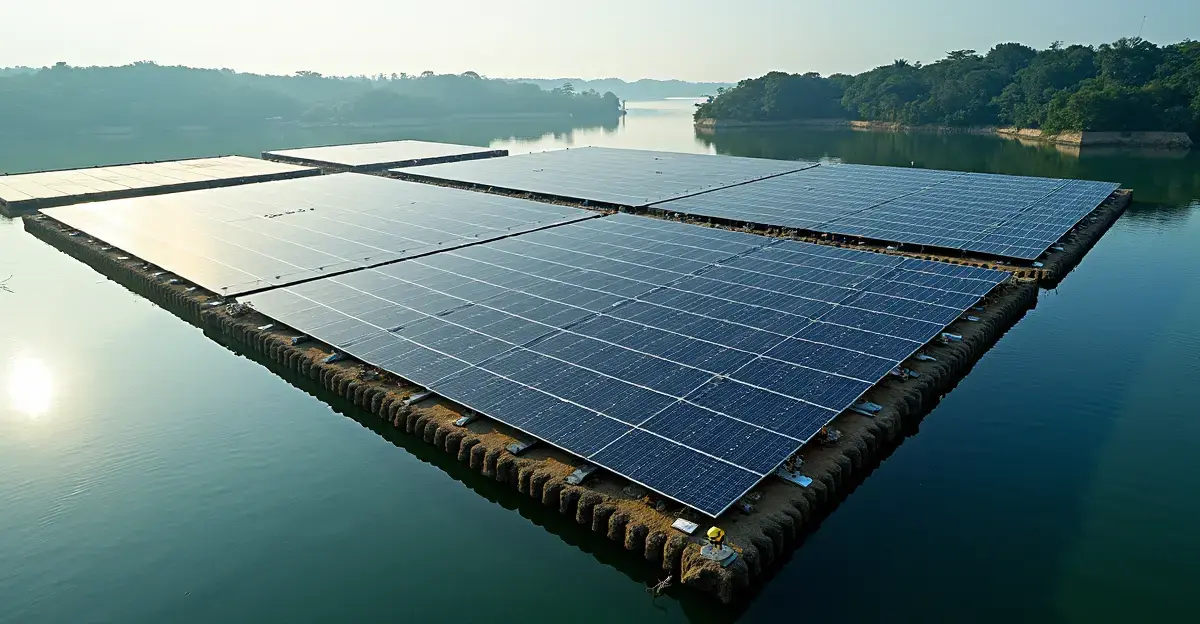
Singapore builds 86 MW floating solar farm on Pandan Reservoir, its largest water body, bringing total floating solar capacity to 296 MW as part of renewable energy strategy.

Singapore's Innovative Floating Solar Solution
Singapore is demonstrating remarkable ingenuity in renewable energy development with the construction of an 86-megawatt floating solar farm on Pandan Reservoir, the city-state's largest water body. This ambitious project represents Singapore's third major floating solar installation and showcases how land-scarce nations can creatively harness renewable energy sources.
Strategic Location and Engineering Excellence
The project, awarded to Singapore-based engineering firm Sembcorp Solar Singapore, will utilize the vast surface area of Pandan Reservoir to generate clean electricity without consuming valuable land resources. This follows two previous successful floating solar installations on Tengeh and Kranji reservoirs, bringing Singapore's total floating solar capacity to 296 megawatts.
"Floating solar projects at reservoirs like Pandan, Tengeh and Kranji are vital for Singapore's land-scarce energy landscape," said Ms. Jen Tan, CEO of Sembcorp Solar Singapore.
Technical Advantages of Floating Solar
Floating solar installations offer unique benefits compared to traditional land-based systems. The water beneath the panels provides natural cooling, which can increase energy production by approximately 2% as solar panels operate more efficiently at lower temperatures. This cooling effect is particularly valuable in Singapore's tropical climate where high temperatures can reduce solar panel efficiency.
Singapore's Renewable Energy Goals
Singapore has set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, aiming to install significant solar capacity by 2030. The country currently generates over 1,000 megawatt-hours of solar energy through various installations, including rooftop arrays. The floating solar projects represent a crucial component of Singapore's strategy to diversify its energy mix and reduce carbon emissions.
According to the International Energy Agency, solar energy development provides "huge longer-term benefits" including enhanced energy security, sustainability, pollution reduction, and lower climate change mitigation costs.
Global Context and Future Prospects
Singapore's approach to renewable energy development serves as a model for other densely populated urban centers facing similar land constraints. The success of these floating solar projects demonstrates how innovative engineering solutions can overcome geographical limitations in the pursuit of sustainable energy.
With all three major reservoirs now hosting solar installations, Singapore faces the interesting challenge of identifying new locations for future renewable energy projects while continuing to advance its green energy transition.

 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Português
Português