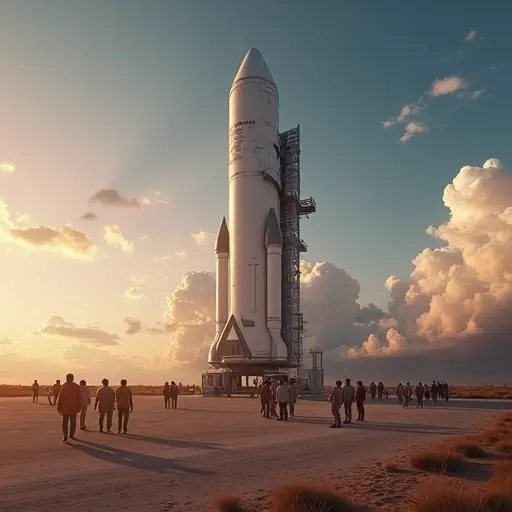
Gravity-Defying Games Enter New Era
Orbital sports arenas are transitioning from sci-fi fantasy to tangible reality. Companies like Cosm are pioneering immersive dome technologies that could serve as prototypes for space-based venues. Their venues in Los Angeles and Dallas feature massive LED screens creating 360-degree experiences, while future Detroit and Atlanta locations hint at the scalability needed for orbital installations.
How Zero-G Sports Work
In microgravity environments, traditional sports transform completely. Basketball becomes three-dimensional with players maneuvering in all directions. New hybrid sports emerge, combining elements of swimming, gymnastics, and acrobatics. Artificial gravity technology, using rotational force to simulate gravity, allows controlled gameplay environments. NASA research shows athletes adapt quickly to microgravity, developing new techniques within hours.
Orbital Infrastructure Progress
Space tourism companies are driving development. Blue Origin and SpaceX plan larger stations with recreational modules. Orbital Assembly's Voyager Station, scheduled for 2027 completion, includes a sports arena in its design. Early demonstrations feature modified versions of volleyball and martial arts where leverage replaces brute strength. The International Space Station recently hosted its first official badminton match, proving competitive sports in microgravity are viable.
Viewer Experience Revolution
Earth-based audiences won't miss the action. Cosm's "Shared Reality" technology provides immersive viewing through domed projection systems. Future broadcasts might include multiple camera drones within orbital arenas, giving viewers player-perspective options. Betting markets for zero-g leagues are already emerging, with major sportsbooks creating odds frameworks for 3D sports.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 French
French
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Portugese
Portugese