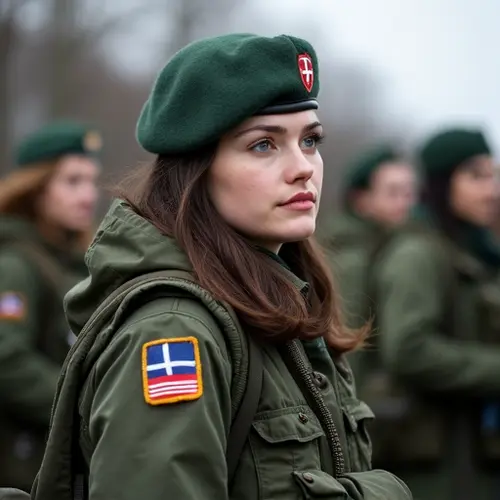
Conscription Returns to European Defense Debate
Russia's invasion of Ukraine, Middle East instability, and geopolitical shifts have reignited discussions about military conscription across Europe. NATO's recent agreement to boost defense spending to 5% of GDP highlights growing security concerns, but manpower shortages remain a critical challenge.
Current Conscription Systems
Nine EU members maintain active conscription: Austria, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Latvia, Lithuania, and Sweden. Croatia will reintroduce a 2-month program in 2026. Models vary from universal service to selective conscription based on skills and motivation.
Countries Considering Reintroduction
Germany's Chancellor Friedrich Merz declared suspending conscription was a "mistake" as the Bundeswehr seeks 60,000 new recruits. Portugal debates reviving its pre-2004 system, while Bulgaria faces 21.8% staffing shortages. Poland aims for 100,000 annual conscripts, and France evaluates a potential €15 billion program. Belgium plans voluntary military service starting 2026.
Opposition to Conscription
Spain's Defense Minister Margarita Robles firmly rejected reinstatement. Slovenia, Slovakia, Albania, and Ireland also oppose conscription, favoring professional armies and voluntary models despite recruitment challenges.
Gender Equality in Service
Denmark recently extended conscription to women, joining Sweden as the only EU countries with gender-neutral systems. Defense Minister Troels Lund Poulsen emphasized the need for more citizens "able to bear arms" as women comprise just 13% of European armed forces.
Future of European Defense
As security paradigms shift, the conscription debate reflects deeper questions about civilian-military relationships in the EU. Solutions may combine voluntary programs, reserve expansions, and selective service models to address defense needs while respecting national preferences.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português



