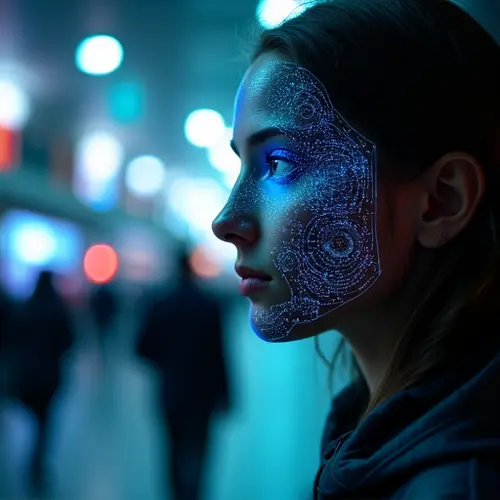

Europe Takes Stand on Biometric Surveillance
The European Union is moving toward banning facial recognition technology in public spaces as part of its landmark Artificial Intelligence Act. This controversial proposal pits privacy advocates against law enforcement agencies who argue the technology helps combat crime. The ban would prohibit real-time biometric identification systems in publicly accessible areas with only narrow exceptions for serious crimes like terrorism or human trafficking.
Balancing Rights and Security
Privacy campaigners welcome the restrictions, citing studies showing facial recognition algorithms exhibit racial and gender biases. "This protects citizens from constant surveillance," said Ella Jakubowska of European Digital Rights. However, police representatives argue the technology helps locate missing persons and identify suspects. Germany's Federal Police recently reported facial recognition helped solve 235 cases in 2024 alone.
Technical Requirements and Exceptions
Under the proposed rules, any permitted use would require judicial authorization and be limited to:
- Terrorism investigations
- Human trafficking cases
- Search for specific violent crime suspects
- Prevention of imminent threats
Post-event analysis using recorded footage would face fewer restrictions but still require compliance with strict data protection standards.
Implementation Timeline
The facial recognition provisions took effect February 2025 as part of the EU's comprehensive AI Act. Member states have until August 2026 to establish national oversight bodies. Several countries including France and the Netherlands are already developing alternative crowd-monitoring technologies that anonymize individuals while tracking crowd movements.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português