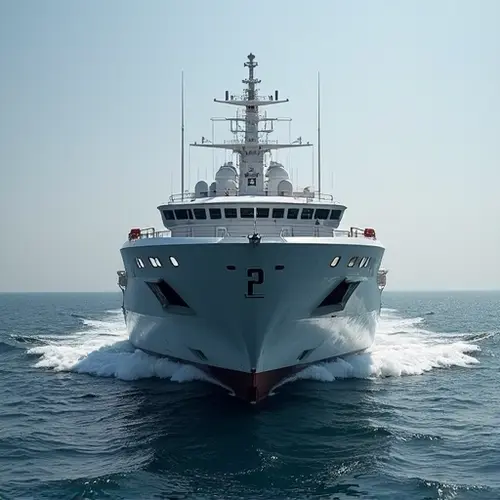

New Era for Shipping as IMO Finalizes Autonomous Vessel Rules
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has officially approved the world's first comprehensive regulatory framework for autonomous ships. After years of development and international collaboration, the Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS) Code establishes safety standards and operational guidelines for unmanned vessels navigating international waters.
What the Regulations Include
The new framework addresses four levels of autonomy: ships with automated processes (Degree 1), remotely controlled vessels with crew onboard (Degree 2), remotely controlled ships without crew (Degree 3), and fully autonomous vessels (Degree 4). Key provisions include:
- Clear definitions of remote operator responsibilities
- Advanced collision avoidance requirements
- Cybersecurity protocols for vessel control systems
- Environmental protection standards
- Emergency response procedures for unmanned operations
Implementation Timeline
The non-mandatory MASS Code will undergo an experience-building phase starting in 2026 before becoming mandatory in 2032. This transition period allows shipping companies to adapt while collecting operational data. "This is about enabling innovation while maintaining our core commitment to safety," stated IMO Secretary-General during the announcement.
Several countries including Norway, Japan, and South Korea have already conducted successful autonomous vessel trials. The Yara Birkeland in Norway became the world's first fully electric autonomous container ship in 2020.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português