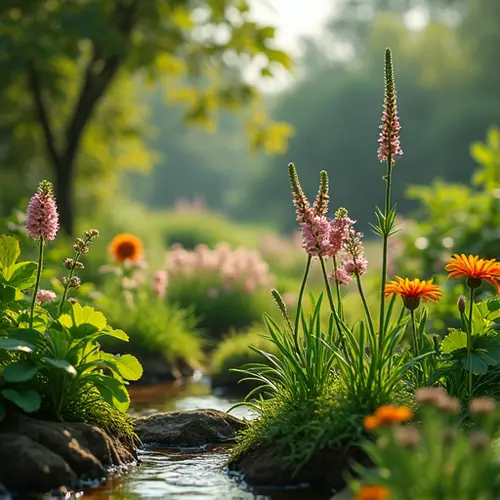

Gardening with Native Plants for Sustainability
As the world grapples with climate change and water scarcity, gardening with native plants has emerged as a sustainable solution. Native plants, which are indigenous to a specific region, require less water, fewer pesticides, and minimal maintenance compared to non-native species. This makes them an ideal choice for eco-conscious gardeners.
Benefits of Native Plant Gardening
Native plants are adapted to local climate conditions, making them resilient to extreme weather. They thrive without the need for excessive watering or chemical fertilizers, reducing the environmental footprint of gardening. Additionally, native plants support local wildlife, including pollinators like bees and butterflies, by providing natural habitats and food sources.
Water Conservation
One of the most significant advantages of native plants is their low water requirement. Unlike exotic species, native plants have evolved to survive on rainfall alone, making them perfect for regions prone to drought. This not only conserves water but also reduces the need for irrigation systems.
Challenges and Solutions
While native plant gardening offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Urban environments often have altered soil conditions and limited space. However, selecting the right native species and incorporating soil amendments can help overcome these obstacles. For example, plants like coneflowers and milkweed are hardy and adaptable, making them suitable for urban gardens.
Getting Started
For those new to native plant gardening, starting small is key. Research local native species and consult with gardening experts or community programs. Many municipalities offer incentives for sustainable gardening practices, including rebates for water-efficient landscapes.
By embracing native plants, gardeners can contribute to biodiversity, conserve water, and create beautiful, low-maintenance landscapes that benefit both the environment and the community.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português