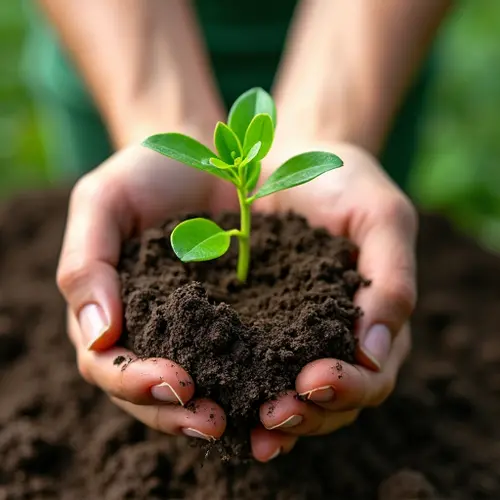

Regenerative Gardening: A Sustainable Approach
Regenerative gardening is a transformative method that focuses on restoring soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and creating resilient ecosystems. Unlike traditional gardening, regenerative practices aim to improve the land rather than deplete it. This article explores key techniques like composting, crop rotation, and planting native species to help you restore your garden's soil at home.
Composting: The Foundation of Healthy Soil
Composting is a cornerstone of regenerative gardening. By recycling organic waste like kitchen scraps and yard trimmings, you can create nutrient-rich compost that enriches the soil. This process not only reduces landfill waste but also promotes microbial activity, which is essential for soil fertility.
Crop Rotation: A Natural Pest Control
Rotating crops annually prevents soil depletion and disrupts pest cycles. For example, planting legumes like beans or peas can fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting subsequent crops. This practice ensures long-term soil health and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers.
Native Species Planting: Supporting Local Ecosystems
Incorporating native plants into your garden supports local wildlife and requires less water and maintenance. These plants are adapted to the local climate and soil, making them more resilient and beneficial for pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Why Regenerative Gardening Matters
Regenerative gardening is not just about growing food; it's about healing the planet. By sequestering carbon, conserving water, and fostering biodiversity, these practices combat climate change and promote sustainability. Whether you have a small backyard or a community plot, adopting regenerative techniques can make a significant impact.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português