China's Desert Transformation Success
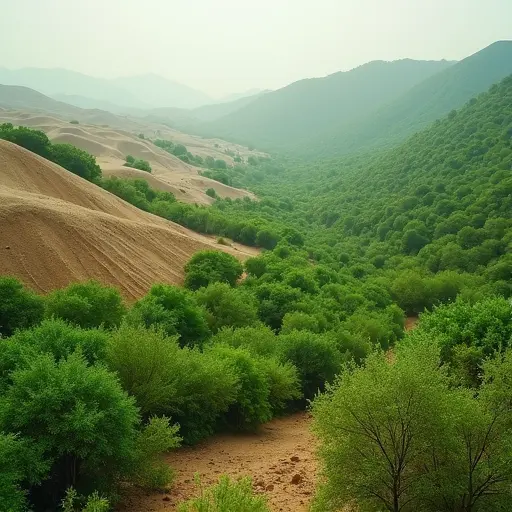
China has achieved a remarkable environmental milestone with its Great Green Wall project, officially known as the Three-North Shelter Forest Program. This massive initiative has successfully converted desert areas into thriving forests, combating the expansion of the Gobi Desert. Since its launch in 1978, the project has planted billions of trees across northern China.
How They Did It
Using innovative techniques like straw checkerboard barriers to stabilize sand and drought-resistant vegetation, China created a 3,000 km green belt around the Taklamakan Desert by late 2024. Satellite data shows desert coverage decreased from 27.2% to 26.8% nationwide, with sandstorms in Beijing dropping by 20%.
Global Impact
The project has inspired similar efforts worldwide, including Africa's Great Green Wall Initiative. Chinese scientists developed specialized planting methods like 'tube planting' that boost sapling survival rates to over 85%. Local communities now harvest fruits and timber from new forests, creating economic opportunities.
Future Plans
By 2050, China aims to expand the green barrier to 4,500 km long and 900 km wide. Recent innovations include drone-assisted seeding and solar-powered irrigation systems. The UN Environment Programme calls it "the world's most ambitious ecosystem restoration project."

 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Português
Português