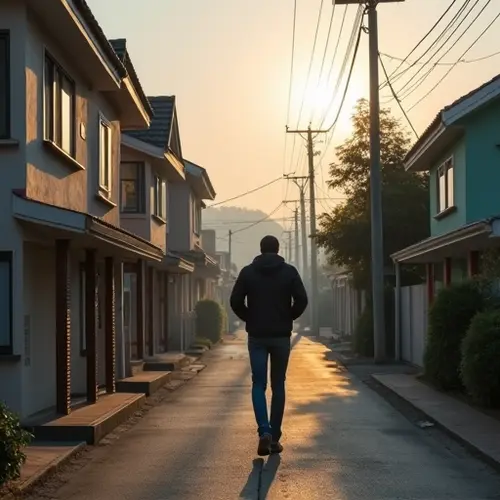

The Global Housing Crisis: A Growing Challenge
The dream of homeownership is slipping further out of reach for millions worldwide, as housing affordability continues to decline in major cities. Rising inflation, soaring interest rates, and stagnant wages have created a perfect storm, making it increasingly difficult for middle- and lower-income families to secure a place to call home.
The Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation has driven up the cost of construction materials, labor, and land, pushing home prices to unprecedented levels. Meanwhile, central banks have raised interest rates to combat inflation, leading to higher mortgage costs. For example, in the U.S., the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate has climbed above 7%, adding hundreds of dollars to monthly payments.
Affordability Metrics Under Strain
Traditional affordability metrics, such as the median house price-to-income ratio, are under severe strain. In cities like Sydney, London, and San Francisco, this ratio has exceeded 10, meaning homes cost 10 times the median annual income. Experts recommend a ratio of 3 or below for a balanced market.
Policy Responses and Solutions
Governments are exploring various solutions, including subsidies for first-time buyers, tax incentives for developers, and zoning reforms to increase housing supply. However, critics argue that these measures are often insufficient to address the scale of the crisis. Affordable housing advocates emphasize the need for systemic changes, such as rent control and public housing initiatives.
The Human Cost
The crisis is not just an economic issue—it has profound social implications. Families are forced to live in overcrowded conditions, commute long distances, or even face homelessness. The psychological toll of housing insecurity is also significant, contributing to stress and mental health challenges.
For more insights, visit J.P. Morgan Research.
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português